
MS Excel: How to use the DVAR Function (WS)
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the Excel DVAR function with syntax and examples.
Description
The Microsoft Excel DVAR function returns the variance of a population based on a sample of numbers in a column in a list or database, based on a given criteria. It is a worksheet function.
The DVAR function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Database Function. It can be used as a worksheet function (WS) in Excel. As a worksheet function, the DVAR function can be entered as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet.
Syntax
The syntax for the DVAR function in Microsoft Excel is:
DVAR( database, field, criteria )
Parameters or Arguments
- database
- The range of cells that you want to apply the criteria against.
- field
- The column to be used in the calculation. You can either specify the numerical position of the column in the list or the column label in double quotation marks.
- criteria
- The range of cells that contains your criteria.
Returns
The DVAR function returns a numeric value.
Applies To
- Excel for Office 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000
Type of Function
- Worksheet function (WS)
Example (as Worksheet Function)
Let's look at some Excel DVAR function examples and explore how to use the DVAR function as a worksheet function in Microsoft Excel:
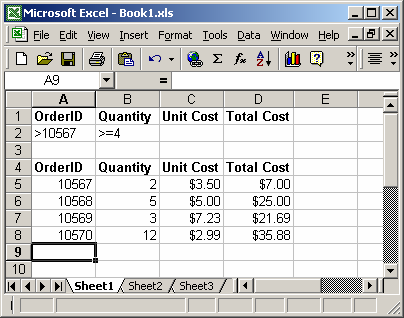
Based on the Excel spreadsheet above, the following DVAR examples would return:
=DVAR(A4:D8, "Unit Cost", A1:B2) Result: 2.02005 =DVAR(A4:D8, 3, A1:B2) Result: 2.02005 =DVAR(A4:D8, "Quantity", A1:A2) Result: 22.33333333 =DVAR(A4:D8, 2, A1:A2) Result: 22.33333333
Using Named Ranges
You can also use a named range in the DVAR function. A named range is a descriptive name for a collection of cells or range in a worksheet. If you are unsure of how to setup a named range in your spreadsheet, read our tutorial on Adding a Named Range.
For example, we've created a named range called orders that refers to Sheet1!$A$4:$D$8.
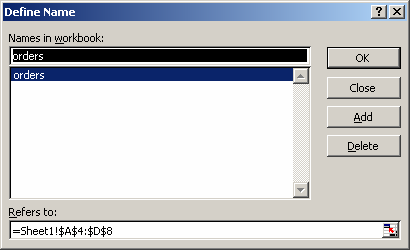
Then we've entered the following data in Excel:

Based on the Excel spreadsheet above, the following DVAR examples would return:
=DVAR(orders, "Total Cost", A1:A2) Result: 55.11443333 =DVAR(orders, 4, A1:A2) Result: 55.11443333
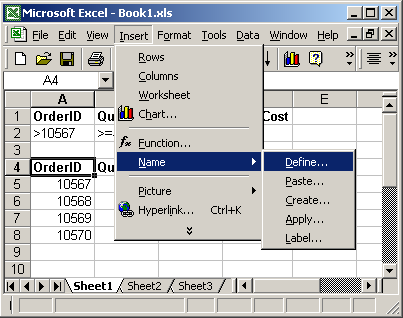
To view named ranges: Under the Insert menu, select Name > Define.
Advertisements



