MariaDB: INTERSECT Operator
This MariaDB tutorial explains how to use the INTERSECT operator with syntax and examples.
Description
Although there is no INTERSECT operator in MariaDB, you can easily simulate this type of query using either the IN clause or the EXISTS clause, depending on the complexity of the INTERSECT query.
First, let's explain what an INTERSECT query is. An INTERSECT query returns the intersection of 2 or more datasets. If a record exists in both data sets, it will be included in the INTERSECT results. However, if a record exists in one data set and not in the other, it will be omitted from the INTERSECT results.
Intersect Query
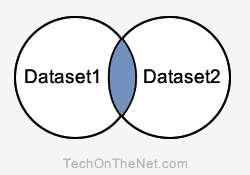
Explanation: The INTERSECT query will return the records in the blue shaded area. These are the records that exist in both Dataset1 and Dataset2.
Syntax
The syntax for the INTERSECT operator in MariaDB is:
SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n FROM tables [WHERE conditions] INTERSECT SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n FROM tables [WHERE conditions];
Parameters or Arguments
- expression1, expression2, ... expression_n
- The columns or calculations that you wish to retrieve.
- tables
- The tables that you wish to retrieve records from. There must be at least one table listed in the FROM clause.
- WHERE conditions
- Optional. The conditions that must be met for the records to be selected.
Note
- There must be same number of expressions in both SELECT statements and have similar data types.
Example - With Single Expression
First, let's explore how to simulate an INTERSECT query in MariaDB that has one field with the same data type.
If the database supported the INTERSECT operator (which MariaDB does not), this is how you would have use the INTERSECT operator to return the common product_id values between the products and inventory tables.
SELECT product_id FROM products INTERSECT SELECT product_id FROM inventory;
Since you can't use the INTERSECT operator in MariaDB, you will use the IN operator to simulate the INTERSECT query as follows:
SELECT products.product_id FROM products WHERE products.product_id IN (SELECT inventory.product_id FROM inventory);
In this simple example, you can use the IN operator to return all product_id values that exist in both the products and inventory tables.
Now, let's complicate our example further by adding WHERE conditions to the INTERSECT query.
For example, this is how the INTERSECT would look with WHERE conditions:
SELECT product_id FROM products WHERE product_id < 45 INTERSECT SELECT product_id FROM inventory WHERE quantity > 1;
This is how you would simulate the INTERSECT query using the IN operator and include the WHERE conditions:
SELECT products.product_id
FROM products
WHERE products.product_id < 45
AND products.product_id IN
(SELECT inventory.product_id
FROM inventory
WHERE inventory.quantity > 1);
In this example, the WHERE clauses have been added that filter both the products table as well as the results from the inventory table.
Example - With Multiple Expressions
Next, let's look at how to simulate an INTERSECT query in MariaDB that returns more than one column.
First, this is how you would use the INTERSECT operator to return multiple expressions.
SELECT contact_id, last_name, first_name FROM contacts WHERE first_name <> 'Sarah' INTERSECT SELECT customer_id, last_name, first_name FROM customers WHERE customer_id >= 50;
Again, since you can't use the INTERSECT operator in MariaDB, you can use the EXISTS clause in more complex situations to simulate the INTERSECT query as follows:
SELECT contacts.contact_id, contacts.last_name, contacts.first_name
FROM contacts
WHERE contacts.first_name <> 'Sarah'
AND EXISTS (SELECT *
FROM customers
WHERE customers.customer_id >= 50
AND customers.customer_id = contacts.contact_id
AND customers.last_name = contacts.last_name
AND customers.first_name = contacts.first_name);
In this more complex example, you can use the EXISTS clause to return multiple expressions that exist in both the contacts table where the first_name is not equal to Sarah as well as the customers table where the customer_id is greater than or equal to 50.
Because you are doing an INTERSECT, you need to join the intersect fields as follows:
AND customers.customer_id = contacts.contact_id AND customers.last_name = contacts.last_name AND customers.first_name = contacts.first_name
This join is performed to ensure that the customer_id, last_name, and first_name fields from the customers table are intersected with the contact_id, last_name, and first_name fields from the contacts table.
Advertisements